How to choose medical furniture
How to choose medical furniture
Equipping a medical facility involves more than just devices, analyzers, and diagnostic systems. Properly selected furniture for a medical office plays a role that is no less important than equipment. It affects the safety of procedures, ergonomics, compliance with sanitary and hygienic standards, and the overall level of patient trust.
Paradoxically, the choice of medical furniture is considered much less often than the purchase of technology and equipment. Meanwhile, it is furniture that withstands daily stress, comes into contact with patients, staff, and medications, and sometimes determines the speed of a doctor's work.
Why medical furniture is a separate category
At first glance, it may seem that it is not necessary to choose furniture specifically for a hospital, and that any office furniture will do. But this is not the case. The medical environment places completely different demands on products:
- Increased resistance to disinfection and repeated processing.
- No porous surfaces where pathogens can accumulate.
- Ergonomics designed for long-term use.
- Safety for patients with limited mobility.
- Resistance to chemical reagents, humid environments, and heavy loads.
- Durability under intensive use.
Therefore, the question “How to choose medical furniture” is not a question of design, but a question of compliance with standards. Not every beautiful cabinet or table from the catalog is suitable for a treatment room or operating room.
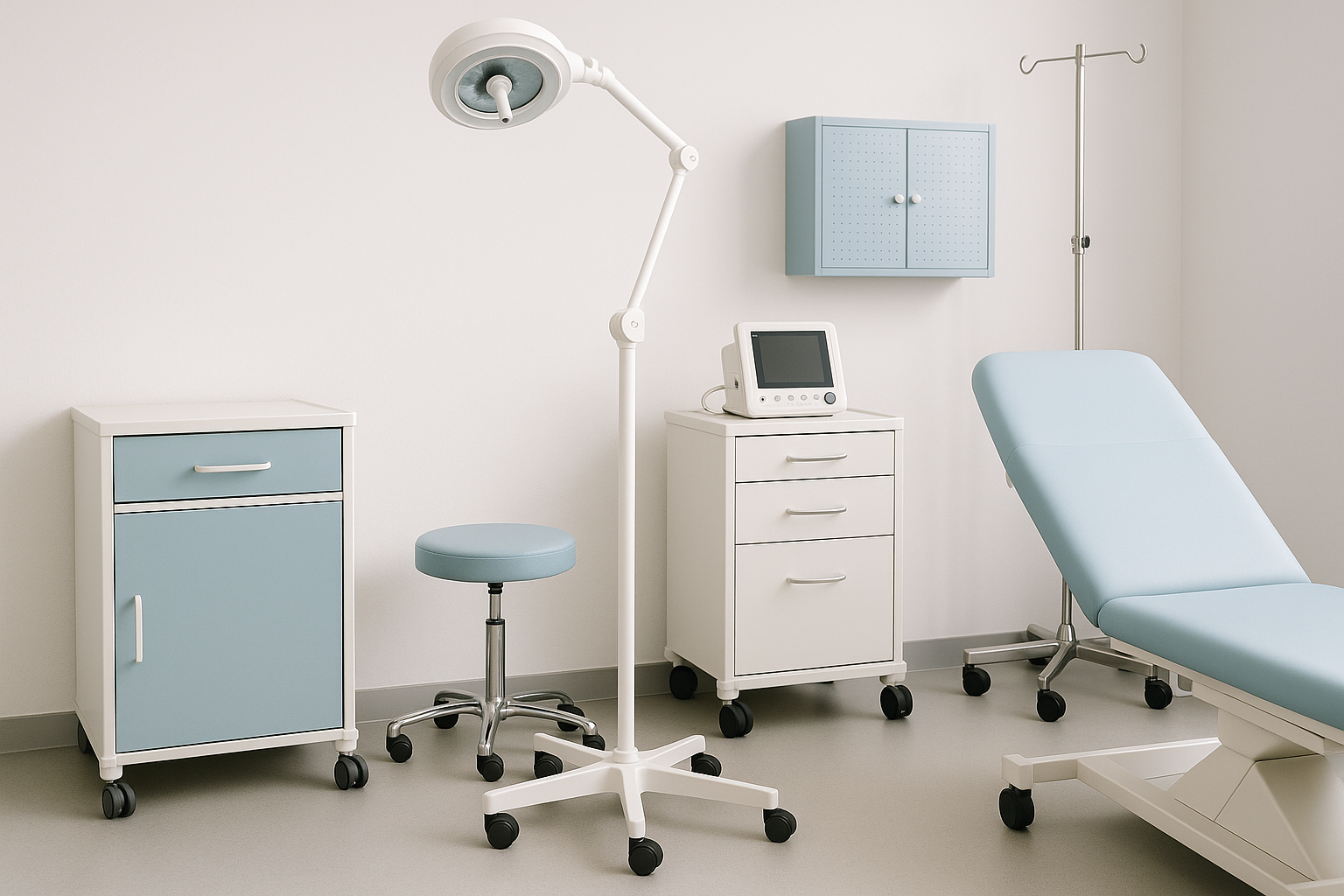
The main types of medical furniture: what a clinic needs
To plan your purchase correctly, it is important to understand the key types of furniture.
Furniture for doctors' offices
This includes desks, chairs, filing cabinets, shelves, and mobile cabinets. Such furniture must be ergonomic, but at the same time comply with sanitary requirements, including smooth surfaces, washable coatings, and no complex elements.
Furniture for treatment and procedure rooms
This includes treatment tables and couches, instrument trolleys, solution stands, metal cabinets, and height-adjustable tables. They must withstand regular treatment with disinfectants and remain resistant to moisture and impact.
Furniture for hospitals and inpatient facilities
This includes patient beds, bedside tables, stands, and rolling systems. The main thing here is reliability and comfort for people who are under round-the-clock supervision.
Laboratory furniture
Work surfaces must be chemically resistant, and structures must be completely stable.
Waiting areas and reception
Here, durability, ease of care, and a neat appearance are important. Patients evaluate the level of a clinic based on these areas.
Key criteria: how to choose medical furniture wisely
Each type of furniture has its own purpose, so there are no universal solutions. Let's move on to the most important thing—the selection criteria.
Materials and their quality
Optimal solutions:
- Powder-coated metal.
- Moisture-resistant laminated chipboard.
- Tempered glass (for display cases).
- High-grade medical plastic.
Avoid furniture with porous or hard-to-clean elements.
Ease of sanitization
Any surface must withstand alcohol solutions, chlorine disinfectants, and frequent cleaning.
This is especially critical for treatment areas.
Ergonomics and safety
Comfortable furniture reduces staff fatigue and eliminates errors. Consider the following:
- Height of tables and chairs.
- Smooth operation of mechanisms.
- Absence of sharp corners.
- Structural stability.
Durability and maintainability
Medical furniture is used daily, so it is important to consider the availability of spare parts and service options in advance.
Practical tips for choosing furniture for different areas of the clinic
- Doctor's office. Doctor's comfort = speed of appointments. The table should be wide enough for a computer, documents, and accessories. The chair should be adjustable, stable, and easy to clean.
- Treatment room: Mobility and sterility are important. The best choices are metal carts, height-adjustable tables, and couches with a moisture-resistant surface.
- Inpatient: Patient beds should have adjustable headrests, side rails, and a sturdy frame. Bedside tables must be stable and free of protruding elements.
- Laboratory: Surfaces must be resistant to acids, alkalis, dyes, and thermal effects.
Mistakes Clinics Make When Choosing Furniture
The five most common mistakes are:
- Buying generic office furniture. As a result, it doesn't hold up to treatment.
- First, they renovate, and then try to "fit" the furniture in. As a result, the structures don't have enough space.
- Choosing cheap materials that aren't designed for intensive use.
- Not taking into account the clinic's growth, resulting in overcrowded offices and insufficient furniture.
- Not analyzing the logistics of the premises. If furniture impedes staff movement, work speed suffers.
These mistakes are more costly than purchasing high-quality furniture from the start.
Where to Buy Medical Furniture: Supplier Requirements
A reliable supplier should provide:
- Official product documentation.
- Warranty.
- Service.
- Consultations on selection.
- Assistance in designing the premises.
An example is Rad Farm, a supplier of advanced medical equipment and supplies for clinics.
How to organize a clinic space based on the furniture you choose
Even perfectly selected medical furniture only works effectively if the clinic space is organized thoughtfully. Many institutions make the mistake of placing furniture and equipment haphazardly, resulting in overlapping patient flows, staff difficulty navigating, and rooms looking overcrowded.
To avoid such situations, it's important to plan in advance the routes for doctors and patients, the placement of consumables, and storage areas for documents and mobile items. For example, carts and treatment tables should be within easy reach, while medication cabinets should be in an area where patients don't have easy access.
Separating functional zones is also key. In offices, it's advisable to designate:
- The doctor's workstation.
- An area for communicating with patients.
- A space for performing procedures.
- Storage areas for instruments and consumables.
Well-chosen furniture helps create a natural order: some items can be mobile, others are stationary, and some serve as "navigation" within the office.
The size of the room is especially important to consider. In small offices, it's best to choose compact models and transformable furniture, while in spacious rooms, a combination of stationary and mobile elements is recommended. Such a well-thought-out organization not only improves staff productivity but also significantly reduces physician fatigue, making the clinic more efficient and comfortable in the long term.
Conclusion
There are many recommendations for purchasing equipment, but the choice of furniture can determine the comfort of doctors and the safety of patients just as much. Properly selected hospital furniture makes the clinic comfortable, organized, and compliant with all standards.
Knowing how to choose medical furniture, a manager can create a space where every detail contributes to quality, sterility, and efficiency, rather than hindering processes. Attention to detail is the foundation of modern healthcare.