Coronary heart disease - causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
Ischemic heart disease is a pathology that occurs due to insufficient blood supply to the heart muscle. The disease manifests itself in chronic syndromes - angina pectoris and heart failure. Among the common complications is myocardial infarction. Dangerous consequences include sudden cardiac arrest. Ischemia is more often detected in men. In 2020, 126 million patients with coronary heart disease were registered in the world.
The prevalence of the disease increases in the older age group, amounting to about 50% among people over 70 years old. According to WHO, heart disease is the leading cause of death. Ischemia is the cause of a third of all deaths worldwide. The number of deaths among men is 5 times higher. Among patients over 50 years old, the difference in the number of men and women is reduced.
What is coronary heart disease
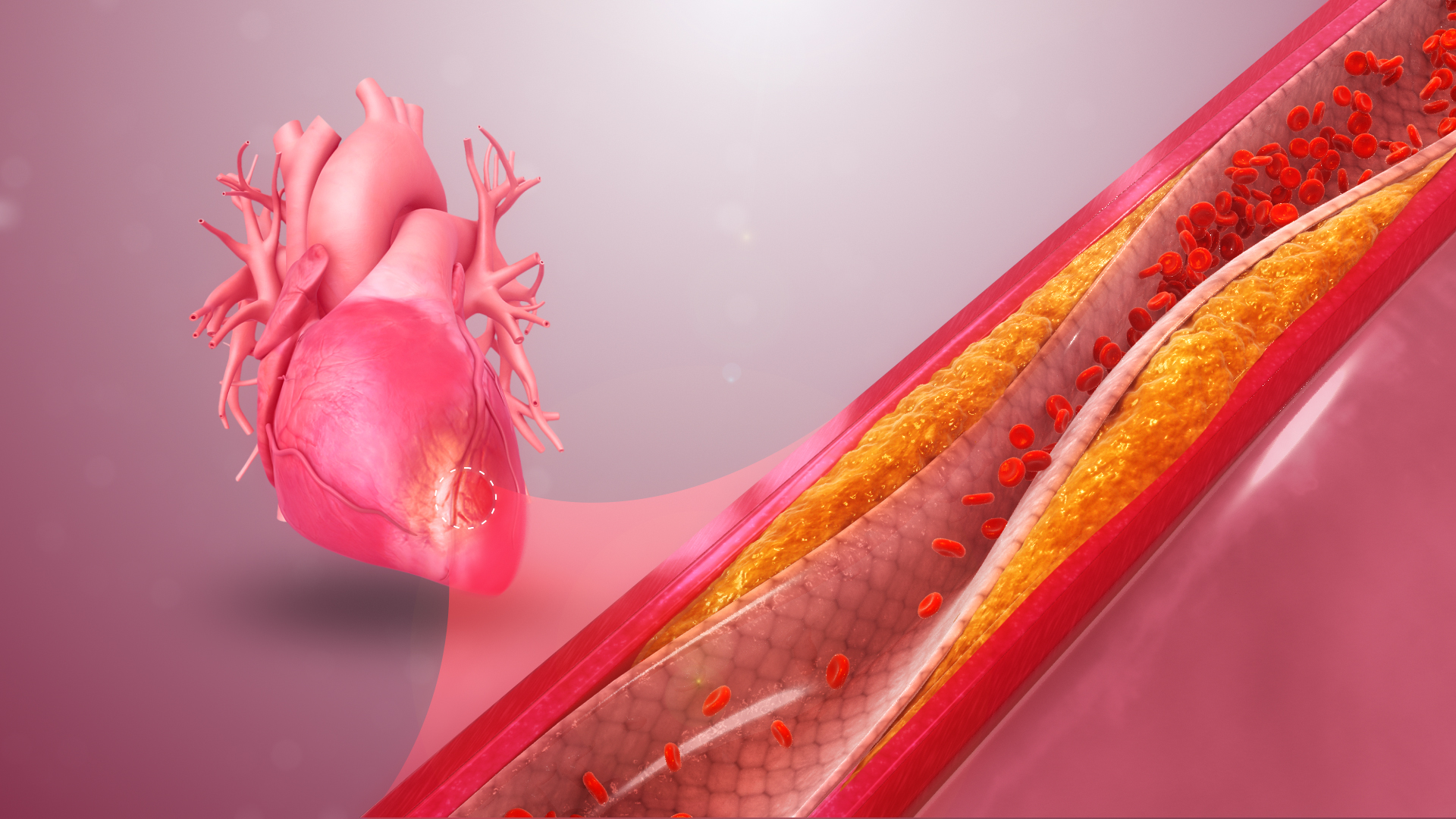
If you want to understand what ischemic heart disease is, you should learn about the features of the heart. For the heart to function normally, a continuous supply of oxygen-rich blood is necessary. Blood flows through the coronary arteries - branches of the aorta. During ischemia, the arteries narrow, which leads to a deterioration in the blood supply to the tissues. As a result, hypoxia develops - a decrease in the concentration of oxygen and oxygen starvation of the tissues. One of the reasons for the narrowing of the vascular lumen is atherosclerosis - the formation of plaques on the walls of blood vessels. In simple terms, due to the narrowed lumen, an insufficient amount of blood flows to the heart.
IHD is dangerous due to complications. The absence of adequate treatment leads to the transition to a chronic form. Long-term courses are accompanied by irreversible changes in the structure of the heart. Patients with a chronic form are often diagnosed with heart failure, which causes limited mobility. Impaired blood supply to the heart muscle is a common cause of disability and sudden death.
Classification of the disease
In medical practice, a classification is used that distinguishes between the types of pathology. Angina pectoris, which is a clinical syndrome of IHD, occupies a special place. Other forms of the course:
- Post-infarction cardiosclerosis. Characterized by the replacement of normal myocardial tissue with cicatricial structures. Replacement occurs in areas of necrosis - tissue death due to lack of nutrition and oxygen. The replacement process lasts for 1-4 months after myocardial infarction.
- Arrhythmic form. Manifested by a violation of the heart rhythm, which occurs in an acute form. Usually, atrial fibrillation is diagnosed.
- Ischemic cardiomyopathy. Pathology develops against the background of a long-term reduction in blood supply to the myocardial tissue. As a result, irreversible changes occur in the tissue structure.
- Myocardial infarction. Manifested by the death of a section of the heart muscle due to an acute lack of nutrition.
The most severe form is coronary death with cardiac arrest, which occurs suddenly and is often associated with an asymptomatic course of coronary heart disease.
Causes of ischemia
Obstruction of the coronary vessels occurs due to spasms of the vascular wall or the appearance of foreign internal structures that block the lumen. The main causes of ischemic heart disease are associated with an increase in cholesterol concentration and the formation of atheromatous plaques. Cholesterol plaques block the vascular lumen and impede the movement of blood flow. Other causes:
- persistent increase or decrease in blood pressure;
- impaired blood clotting with increased thrombus formation;
- thyroid pathologies.
Less often, the causes of coronary heart disease are due to spasm of the arteries that feed the heart muscle, which leads to the development of vasospastic angina. In patients with vasospastic angina, fixed obstruction (obstruction) in one or more coronary arteries is often detected. The pathology is characterized by anginal attacks that occur mainly at night in a state of rest. It manifests itself as severe pain in the chest area radiating to the shoulders, arms, and shoulder blades. Arterial spasm occurs due to increased vascular tone and as a result of an excessive response to stimuli that cause narrowing of the vascular lumen. Atherosclerosis develops against the background of dysfunction of the endothelial lining of blood vessels. Vascular damage in atherosclerosis occurs unevenly. It usually occurs at the bifurcation site - bifurcation of the arteries. Plaque growth is accompanied by narrowing of the vascular bed. As a result, blood supply to the heart muscle deteriorates and ischemia develops. Sometimes a cholesterol plaque ruptures with the formation of collagen and other components that provoke the formation of blood clots. The coagulation cascade causes acute thrombosis. The thrombus blocks the vascular bed. As a result, the volume of blood flow decreases, and in severe cases, the blood supply to the tissues stops.
Another cause of coronary heart disease is an increase in the size of the heart, which occurs against the background of arterial hypertension. Stress and depression have a negative effect on the condition and functions of the heart muscle. Other modified provoking factors:
- consumption of excessive amounts of animal fats;
- abuse of alcoholic beverages;
- smoking;
- sedentary lifestyle, physical inactivity;
- increased concentration of C-reactive protein in the blood;
- psycho-emotional overstrain.
Increased concentration of C-reactive protein indicates inflammatory processes and unstable position of the atherosclerotic plaque. Among the non-modified factors, it is worth noting hypothyroidism (insufficient production of thyroid hormones), abdominal obesity (fat deposits in the abdominal area), bronchial asthma (non-infectious inflammatory process in the lung tissue), diabetes mellitus, impaired carbohydrate metabolism and glucose tolerance in the anamnesis. Other unmodifiable risk factors:
- Age over 55;
- Male gender;
- Cholelithiasis;
- Genetic predisposition.
The disease often develops against the background of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Considering that cardiac ischemia develops as a result of fluctuations and increases in blood pressure, patients at risk should undergo daily diagnostics. Blood pressure is assessed using tonometers.
Symptoms of ischemia
Symptoms appear when the degree of narrowing of the feeding arteries exceeds 50%. Chronic angina is the leading symptom, which is characterized by pain localized in the chest area. Painful sensations in the sternum are squeezing and compressive in nature. Other manifestations of angina:
- Feeling of suffocation, lack of air, nausea;
- Feeling of heaviness in the chest;
- Incorrect heart function with interruptions;
- Dizziness, clouding of consciousness;
- Fear of death.
Painful sensations often spread to the shoulders, arms, and upper abdomen. An attack of angina usually lasts about 15 minutes, less often it passes within 30 minutes. It is often accompanied by a panic attack. Often the pain appears as a result of increased physical exertion. After the load is eliminated, the pain and other symptoms gradually regress. Further development of the disease causes increased sensitivity to loads. Subsequently, an attack occurs with little physical effort. Signs of coronary heart disease in women are often less specific:
- increased fatigue, chronic fatigue;
- sleep disturbance, difficulty falling asleep, restless, interrupted sleep;
- indigestion - discomfort after eating;
- increased anxiety, a feeling of nervousness and restlessness without obvious reasons.
With angina, the number of heart contractions and respiratory movements increases. Angina can remain stable or progress. In the second case, a gradual increase in the frequency and duration of attacks is observed. If myocardial infarction occurs, the pain does not go away after eliminating the load and taking medications. Other symptoms of coronary heart disease:
- increased sweating;
- low or high blood pressure;
- increased fatigue, chronic feeling of tiredness;
- slowing down, acceleration, disturbance of the sinus pattern of the heart rhythm;
- shortness of breath, which is accompanied by disturbance of the respiratory rhythm and difficulty inhaling;
- paleness of the skin.
An attack of ischemia is often preceded by a feeling of discomfort in the sternum area, emotional lability - sharp mood swings. With sudden coronary death, the patient loses consciousness. There is no pulse in the carotid artery area. Breathing stops, the pupils dilate, the skin takes on a pale gray tint.
Diagnosis of ischemia
To make a diagnosis, the doctor examines the patient, studies the anamnesis and complaints. Laboratory diagnostics in the form of a blood test shows the lipid profile, enzyme levels, electrolytes and hormones. A coagulogram allows you to evaluate the parameters of blood clotting. Instrumental diagnostics are carried out to identify structural changes and functional disorders in the work of the heart. During radiography, the size of the organ and areas of damage to muscle tissue - the myocardium are revealed. Instrumental diagnostic methods include daily Holter monitoring, daily measurement of blood pressure indicators, electrocardiography, echocardiography, stress tests. The main parameters that help to make a diagnosis:
- blood pressure indicators;
- characteristics of heart murmurs;
- heart rate.
Diagnostics of coronary heart disease is based on the study of the heart rhythm and other functional indicators. Doctors use electrocardiographs to obtain information about the electrical activity of the heart muscle and assess the condition of the myocardium. Echocardiography is an ultrasound examination of the heart muscle, performed to identify areas with impaired blood flow.
For early detection of abnormalities in the work of the heart, Holter ECG and blood pressure monitors are used. Holter monitoring involves recording an electrocardiogram throughout the day. The recording is carried out under normal lifestyle conditions. The study shows changes in the work of the heart during the day, which may not be displayed during a one-time electrocardiography.
One of the effective diagnostic methods involves the use of a stress system, which shows the characteristics of heart activity during physical exertion. In cardiology, stress tests are carried out, which allow identifying signs of coronary heart disease. Controlled physical activity is stress for the body, which provokes reactions from the heart and blood vessels.
During the study, functional disorders are detected that are not noticeable at rest. Stress tests are carried out to analyze the compensatory and adaptive abilities of the body to stress. A common test is carried out on a moving track - a treadmill. It is possible to change the angle of inclination and speed of the track, which allows studying the work of the heart under loads of varying intensity. Detection of pathology at an early stage increases the effectiveness of treatment.
Methods of treatment of coronary heart disease
If you notice symptoms of the disease, do not delay a visit to the doctor. Discomfort in the chest area is the initial sign of the development of the disease. Treatment in the early stages is reduced to taking pharmaceutical drugs, lifestyle and diet correction. The doctor will tell you how to treat cardiac ischemia during the appointment. The tactics of therapy depend on the severity of the disorders and changes that have occurred in the myocardium. In the early stages, conservative therapy is indicated. The doctor prescribes drugs that eliminate spasms of the vessels that feed the heart. In a comprehensive therapy program, drugs are used:
- to normalize blood pressure;
- to lower cholesterol levels;
- to prevent the formation of blood clots;
- to eliminate psychoemotional stress and restore sleep.
In acute thrombosis, fibrinolytic drugs are prescribed that destroy blood clots. Beta blockers are indicated to reduce the severity of angina symptoms. Taking beta blockers reduces the risk of death after myocardial infarction. Drugs that prevent blood clots improve the results of therapy.
Physical therapy is prescribed to train the heart muscle.
If conservative therapy is ineffective, an operation is performed - angioplasty, which is used to expand the lumen of narrowed vessels. During the operation, the surgeon places a stent inside the vessel - an elastic metal or plastic cylindrical element that prevents narrowing of the vascular lumen. If angioplasty does not give the desired effect, aortocoronary bypass is performed. During the operation, the surgeon removes part of the affected vessel and installs a shunt - an artificial vessel.

How long do people live with coronary heart disease
It is difficult to give a clear answer to the question of how long people with coronary heart disease live. The answer depends on the severity of the disorders and damage to the heart muscle, the presence of adequate treatment and lifestyle. If after diagnosis the patient does not change his diet and lifestyle, does not undergo treatment and does not follow the doctor's recommendations, the life expectancy is no more than 5 years. Every tenth patient who does not undergo treatment dies due to cardiac arrest. To improve the prognosis, you should follow the rules:
- give up bad habits;
- get measured physical activity, play sports;
- regularly take the medications prescribed by the doctor;
- exclude fatty foods with high calories from the diet;
- increase the proportion of vegetables and fruits in the menu.
As part of prevention, it is important to regularly consume plant fiber, vitamins E, C, D, and Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. An effective preventive measure is the absence of stress, physical and psycho-emotional overstrain. Patients at risk are recommended to undergo examination at least once a year. Provided that recommendations are followed, the life expectancy of patients with coronary heart disease increases significantly. In medical practice, there are known cases of longevity up to 90 years.


