Densitometry, what is it, what diseases does it diagnose, how to prepare
Densitometry – is a modern method for diagnosing bone density. The examination helps monitor health and reduce the risk of injury. The method is widely used in medical practice and sports. Density assessment is necessary as part of the diagnosis of osteoporosis, prevention of pathological complications and monitoring the effectiveness of therapy.
Osteoporosis is characterized by a decrease in bone density due to the loss of calcium and minerals that provide tissue hardness. Normally, calcium is responsible for the strength characteristics of bones and resistance to damage – fractures and crack formation.
Densitometry: reasons to do
Osteoporosis – is a common disease that is detected in 70% of people over 90 years of age. Densitometry analysis – is a mandatory stage of diagnosis. In the age group over 60 years of age, the proportion of patients with osteoporosis is 10%. About 1 million new cases of the disease are diagnosed annually around the world. In total, there are more than 250 million patients with osteoporosis. Complications and consequences:
damage to the joints, mainly the hip and knee, with the development of pain and limited mobility;
susceptibility to bone fractures – a small blow can cause serious damage to the musculoskeletal system;
skeletal deformation with changes in the normal shape and structure of the musculoskeletal system;
disability – about 50% of patients become disabled.
One of the main risk factors – is a decrease in bone strength. Densitometry shows how likely the disease is to develop. Bone tissue is formed during life. At the first stage of life, bone volume increases. The growth stage is replaced by a period of stabilization and then reduction in bone mass volume. Physiological loss of bone volume begins in women from the age of 35, in men – from the age of 45. Losses in the initial stages amount to 0.3-0.5% during the year. In women with menopause, the rate of bone loss increases to 2-3% throughout the year. The pace is maintained until the age of 70. During life, women lose 35-50% of bone tissue, men – 20-30%. The lower loss rate in men is due to increased levels of estrogen and testosterone compared to the female body.
An increased risk of fractures is associated with bone loss. Severe consequences are typical for fractures of the femoral neck and spine. The mortality rate within 1 year after a fracture of the femoral neck is more than 50%. Among surviving patients, 33% are bedridden. Timely studies for osteoporosis will help avoid severe consequences and maintain health. To carry out densitometry, special – densitometer devices are used.
Densitometry: features and indications
Every patient who is at risk of developing osteoporosis knows what densitometry is. This is a mandatory study prescribed by an endocrinologist, rheumatologist or orthopedist. During the diagnosis, the degree of mineralization of bone structures is determined. One of the advantages of the – procedure is instant results. Densitometers are designed to scan all parts of the musculoskeletal system – of the spine, forearms and limbs. Main indications for the examination:
age over 40 years for women, 50 years for men;
past pregnancy;
history of frequent bone fractures;
parathyroid diseases;
hormonal imbalance;
bone fractures due to minor injury;
regular use of pharmaceuticals – tranquilizers, glucocorticosteroids, oral contraceptives, psychotropic drugs;
metabolic disorder – diabetes mellitus and a history of obesity.
The densitometry study is indicated for professional athletes; people who actively engage in sports prefer extreme types of recreation. The examination is prescribed to patients who suffer from chronic diseases that affect the condition of bone tissue. Patients with rheumatoid arthritis, chronic nephritis, and hepatitis are at risk.
Densitometry: spp
The density of matter in physics is calculated by dividing mass by volume. In medicine, special – densitometer devices are used. Bone densitometry can be X-ray and ultrasound. In the first case, X-rays are used to study bone tissue, in the second – ultrasonic waves.
Ultrasonic densitometry is based on the ability of the bones of a spongy structure to conduct sound vibrations. The lower the density of bone structures, the fewer waves are reflected and returned to the sensor. One of the main advantages of the – safety method for the patient. The person being examined is not exposed to ionizing irradiation. The ultrasound technique is indicated for pregnant and lactating women. Disadvantages:
Increased sensitivity to the conditions (sensor position angle, degree of moisture in the skin, pressure on the sensor at the time of examination).
Difficulties in tracking dynamics during re-screening. Bone density is not the same in different areas. When comparing the results of two studies, errors are possible.
The design of the device allows you to study the density of the calcaneus or wrist bone. As part of the diagnosis of osteoporosis, the study of bone tissue of the femur and vertebrae is of great importance.
X-ray machines are single-photon and two-photon. The degree of X-ray absorption increases with increasing tissue density. X-ray diagnostics are highly accurate. X-ray densitometers can detect a slight decrease in – density by up to 2%. Thanks to the information received, the doctor prescribes treatment in a timely manner to prevent further reduction in bone volume. Early diagnosis improves therapy outcomes. Adequate therapy in some cases leads to complete restoration of normal bone density.
Another advantage of X-ray densitometry – is the ability to study the density of structures of the spine and femoral neck, which are surrounded by volumetric soft tissues. The examination of bones covers a significant area of tissue, which makes it possible to obtain objective information about density. The doctor compares research results at different times and monitors the dynamics of changes. The readings of X-ray densitometers are practically independent of the human factor – of the operator’s knowledge and skills. X-ray two-photon densitometry – «gold» standard in the diagnosis of osteoporosis and osteopenia.
Densitometry: procedure
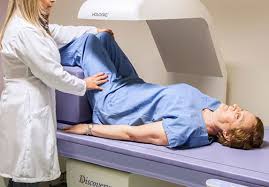
Densitometric examination allows you to study the condition of bone structures in certain areas or in all parts of the musculoskeletal system. This is a painless, non-invasive procedure that does not require preparation. Before the examination, the jewelry must be removed. For diagnostics, loose clothing that does not restrict movement is suitable. Avoid clothes with buttons, buckles, and metal decorative elements. It is prohibited to take calcium supplements 24 hours before the examination. How Densitometry is performed:
the patient lies down on the couch;
the doctor establishes the X-ray source above the patient;
the source runs along the patient's body, determines bone density in different areas and transmits information to the display.
The procedure lasts 10-20 minutes. Densitometry results can be obtained on the day of the study. Modern densitometers with intelligent functions independently calculate indicators. Information is available as digital values, graphs and diagrams.