Defibrillator: what types there are and the principle of work
Fibrillation is one of the disorders of the heart, when instead of full-fledged, normal contractions, there are frequent and non-rhythmic contractile movements. The condition is typical for a contraction rate of more than 300 beats per minute. As a result, blood is worse at pushing through the blood vessels, which impairs circulation.
Defibrillation is a contact action on the sternum in the heart area with an electric shock. The procedure is carried out to eliminate severe arrhythmias that are not amenable to being controlled by pharmaceutical drugs. It is included in the list of resuscitation measures aimed at eliminating severe arrhythmias. Defibrillation is not performed in case of complete cardiac arrest. In this case, an effective solution is cardiopulmonary resuscitation, which includes indirect cardiac massage and artificial respiration.
Defibrillation is performed by an emergency physician or resuscitator using special equipment. A defibrillator is a device that restores normal heart rhythm. Indications for the procedure are ventricular fibrillation and ventricular flutter. In the first case, it is a chaotic contraction of the ventricles with a frequency of more than 300 beats per minute. Due to the accelerated rate of contraction, the ventricles do not have time to fill with blood, which leads to a significant disruption of blood circulation. The patient may not have a pulse in the area of the extremities.
Ventricular flutter is a condition similar to fibrillation. The only difference is in the rhythmic, not chaotic contraction. The doctor's task in this situation is to prevent the consequences of ventricular fibrillation (loss of consciousness, seizures, irreversible damage to brain tissue), for which a defibrillator is needed. Cardioversion is performed in cases of atrial flutter and fibrillation.
Defibrillation refers to resuscitation measures, cardioversion is performed as part of emergency care for the patient or routinely in case of recurrent, prolonged arrhythmia attacks. Electric discharge is used in case of chaotic heartbeat and in case of unconsciousness of the patient.
A contraindication for defibrillation is cardiac arrest. In this case, the procedure is not effective. If the arrest was due to arrhythmia after restoration of cardiac activity by cardiopulmonary resuscitation, a defibrillator may be used to normalize the rhythm.
How defibrillation is performed
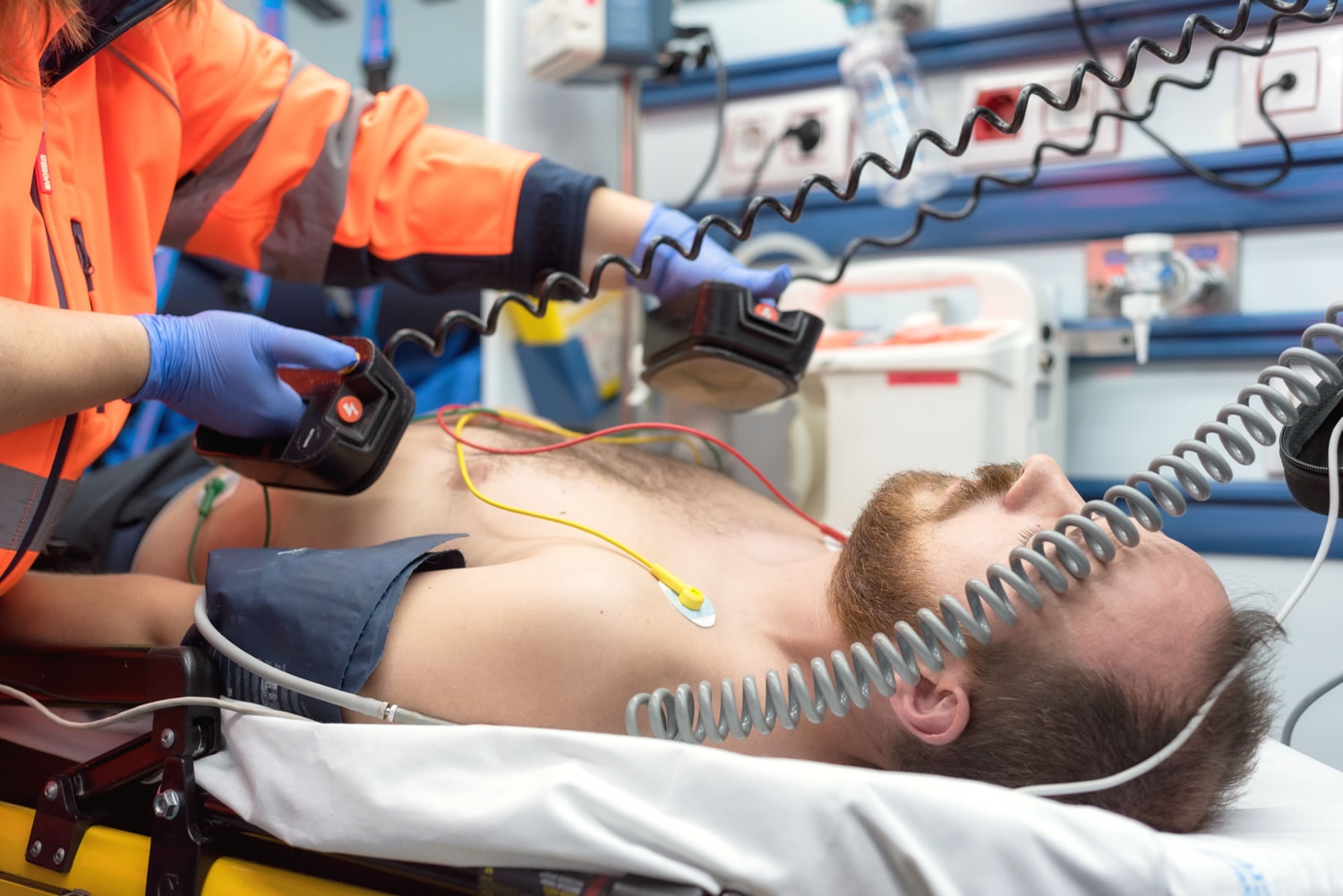
The procedure is performed after a health care provider is satisfied that the patient has a complex arrhythmia or diagnoses unconsciousness. In order to restore normal blood flow, it is necessary to get the heart working again. This is what a defibrillator is for. The device is used to eliminate arrhythmias. The technique of working with a defibrillator:
- Laying the patient on a flat, hard surface.
- Freeing the chest from clothing.
- Treating the device electrodes with conductive gel.
- Applying the electrodes to the patient's chest.
Correct operation of the defibrillator depends on compliance with the rules of operation. Apply the electrodes according to medical protocol and instructions. The electrode marked APEX is placed in the area of the upper heart, the electrode marked SPERNUM - in the area of the right clavicle. The electrodes are pressed against the body, applying a force of about 10 kg. The physician turns on the defibrillator and selects the charging power. In some models, the calculation of power is automatic. To start the device, the doctor presses a button. After the session, the pulse is checked. If the patient is connected to an electrocardiograph, the display shows indicators of cardiac activity.
What discharge in the defibrillator, the doctor chooses. For biphasic models, the indicator is 150-200 J, for monophasic models - 360 J. Evaluation of the heart rhythm is carried out 2 minutes after the session. If there is no effect after the first discharge, the procedure is repeated with an increase in power. The maximum power is 360 J. The voltage is 4000-7000 V. Depending on how many volts the device gives out, the power of the effect differs.
The heart-starting device is used to help patients with obvious signs of circulatory failure, which is accompanied by loss of consciousness, lack of pulse and respiration.
Medical defibrillator: device and principle of operation
To understand what a defibrillator does, you need to understand the principle of operation of the device. Defibrillator - a device that generates and transmits electrical impulses. There are differentiated stationary, portable and portable models. The device of the defibrillator assumes a design of blocks:
- Condenser (accumulator) and converter of electrical energy.
- Electrodes. The device is equipped with one or two electrodes.
- Monitor, which displays the curves of the cardiogram, the frequency of heart contractions, the level of saturation, the frequency of respiratory movements.
- Control panel.
- Cable for connection to the network 220V.
The speed of passing the pulse through living tissue is 0.01 seconds. Built-in electrocardiograph with monitor allows you to assess the effectiveness of rehabilitation measures. The principle of operation is based on the accumulation of energy in the capacitor, which occurs when the device is connected to the electrical network or an external battery. In stand-alone models, charge accumulation occurs due to the built-in battery. Discharge of the plates leads to the formation of a single damped, oscillating pulse.
To understand how the defibrillator works, you need to visualize the scheme of the device. The mains converter takes the 220V voltage from the electrical outlet and converts it into a direct current with a voltage reading of 18V. The output voltage is fed to the charging unit of storage capacitors.
Types of defibrillators
Depending on the shape of the pulse, there are types of defibrillators - monophasic and biphasic. Monophasic models conduct an electric current in a single direction. Biphasic device generates an alternating current, which is transmitted from one electrode to another and then moves in the opposite direction to the myocardium. Modern devices predominantly implement the biphasic principle of operation. The advantage of biphasic models is a lower risk of damage to living tissues by the current, which is due to the lower energy required to restore the normal rhythm. Taking into account the nature of control, types are distinguished:
- Manual. Features - complex control, affordable price. Usually designed to equip the rehabilitation department, intensive care wards, surgical unit.
- Automatic. Independently determine the heart rhythm violation, select the power of the charge, easy to operate. They are distinguished by their compact size, suitable for equipping emergency vehicles and independent use by relatives of patients. Disadvantages - high price, limited range of additional settings.
- Universal. Assume manual control and automatic mode of operation.
In models with manual control provides the ability to select the mode (synchronous, asynchronous), power and time of action discharge. Manual models are usually used in medical institutions. Maintenance of the device requires professional skills and experience.
Automatic external defibrillators independently analyze the heart rhythm without the participation of the operator and confirm or deny the need for resuscitative measures. Automatic models can be used by people without special medical training to provide emergency assistance to relatives suffering from heart disease. It is advisable to use an automatic device until the arrival of ambulance personnel. Many models have voice and text prompts that simplify operation.
To understand what a defibrillator monitor is, you need to imagine a model equipped with a display that shows information about the mode of operation and indicators of the patient's cardiac activity. Defibrillator monitor is equipped with a built-in electrocardiograph, which reads data on the operating parameters of the heart and displays it on the display. Heart rate, saturation, body temperature and blood pressure, as well as a graph of the cardiogram, are available to the physician. Defibrillator monitor is designed for use in medical facilities.
The main purpose of the stationary model is medical assistance to patients in intensive care wards and intensive care units. Portable device for starting the heart is characterized by small size, suitable for equipping emergency vehicles and home use. Most portable models are adapted for users without medical knowledge and skills.
Depending on the location of the device relative to the patient's body, external and internal models are distinguished. Internal devices - pacemakers, implanted in the chest cavity. Pacemaker controls the rhythm of the heart in automatic mode. If necessary, it generates a charge that restores a normal heartbeat. External defibrillators are equipped with electrodes that are applied to the surface of the patient's chest during the procedure.
Cardiac synchronized devices are designed to perform defibrillation and cardioversion, a therapy in which the charge is automatically synchronized with heartbeats.
Rules for defibrillator use
The medical defibrillator is installed in intensive care units, surgical units, intensive care wards. The device refers to special medical equipment, which is used according to the attached instructions. Improper use of the device, which is under high voltage, can lead to injury to the patient and staff. Rules of use of the defibrillator:
- The device is to be serviced by trained personnel who have been instructed. The procedure is usually performed by cardiologists or emergency personnel.
- It is forbidden to operate the device without first reading the instruction manual and learning the controls and functions.
- The device must be connected to a fixed socket outlet equipped with a grounding terminal. The absence of a protective earth connection on the socket means that the general power supply system cannot be used. In this case, the resuscitation device is connected to an external battery.
- Electrical medical equipment connected to the patient should be disconnected before the procedure unless it is defibrillation-proof.
- Keep conductive gel away from the electrode handles to prevent electric shock.
- Ensure that the exposed parts of the patient's body do not come in contact with metal parts of the bed to prevent the formation of unwanted conductive pathways.
- Before pressing the start button, make sure that the patient is unconscious, has an unstable heart rhythm, no pulse and no respiratory activity.
- It is forbidden to disassemble the device by yourself. There are no blocks and parts in the design, which are maintained by the operator. Diagnosis and repair are performed in the service center.
When a defibrillator is used, the doctor preliminarily notifies the staff about the upcoming discharge. Surrounding people should move away to a safe distance. If the heart rhythm cannot be restored after the fourth attempt, the physician will declare the patient dead.
For the operator's safety, the device should not be started in conditions of increased oxygen concentration in the ambient air, as well as in the vicinity of flammable substances - anesthetics, alcohol, gasoline. When the device is used, high humidity should be avoided. Do not resuscitate with the defibrillator outdoors during precipitation or near bodies of water. Do not use the device when the patient is lying on wet ground.